Megan Warburton, 34, who lives in Southend, and her husband Chris, 39, first began trying for a baby in 2016. Tests at a private clinic revealed azoospermia, meaning a zero sperm count, so they went back to their GP for an NHS referral. In January 2020, Chris had an operation to extract sperm, which was then successfully frozen, but when Covid hit, their appointment to see a consultant was delayed.
“And then it was delayed again, and again,” says Chris. “We’d get another letter and then another – we just started dreading them.” After a while, the couple decided to take matters into their own hands, attending a private low-cost fertility clinic, abc IVF.
“I was 32 when we started treatment, which isn’t that old, but we’d already been trying for four years,” says Megan. “With all the delays I was concerned we might miss our chance.” After one round of IVF, she became pregnant and now has a son, Joe, 11 months. “It’s hard to say how it feels,” she admits. “Extreme happiness is an understatement.”
When Megan was four months pregnant, the couple received another NHS letter, offering them an appointment in three months’ time. “They obviously hadn’t updated their records,” she says. “I thought, imagine how upset I would have been if I hadn’t been able to go privately.”
Yet for those who cannot afford to go private and are seeking NHS fertility treatment, Covid has led to long waiting lists and the prospect of not being able to have a family at all. New research released last week by the Human Fertilisation & Embryology Authority (HFEA), in The Impact of Covid-19 on Fertility Treatment 2020 report, reveals while private fertility services have been quick to bounce back, recovery within the NHS has been slower.
There was a 38 per cent decrease in the number of NHS-funded IVF cycles for patients aged 18-34 from 2019 to 2020, compared to a 13 per cent decrease among privately funded patients aged 18-34. For women aged 35-40, NHS-funded cycles saw a 32 per cent drop, compared to 12 per cent drop in self-funded IVF.
“In comparison to private care, NHS clinics more commonly had staff redeployed to support other services which could have led to clinics being slower to restart treatment,” Julia Chain, chair of HFEA, points out. “High waiting times for tests or surgery may have delayed treatment too; an aftershock of Covid-19 that we expect will continue for at least another 12 to 24 months.”
Data from the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists’ (RCOG) April report, shows gynaecology waiting lists have seen the biggest increase of all medical specialities, with women in the UK facing prolonged waits for appointments, diagnoses and treatments, which are often needed before they can move forward with fertility treatment.
Similarly, the Fertility Network UK’s November 2021 survey found that 58 per cent of the 400 patients surveyed had experienced issues accessing treatment as a result of the pandemic. Patients reported widespread delays in diagnostic testing, including blood tests and semen analysis, and also various surgical procedures from laparoscopy to surgical sperm retrieval.
Delays ranged from months to more than two years, with many patients forced to repeat tests that were out of date by the time they had been able to access treatment; others reported delayed or cancelled appointments, resulting in added stress and anxiety.
“Treatment delays have that extra impact, for two reasons,” says Fertility Network UK’s spokesperson, Dr Catherine Hill. “One, because time is of the essence, your biological clock is ticking. But it’s also will you be able to access NHS funding, because the rule is women under 40 get access to treatment. Some clinical commissioning groups set their own criteria, so in certain areas you have to be under 35.”
When it comes to treatments timing is vital, with the likelihood of success decreasing with each passing year. Fertility declines with age, due to declining egg count and quality, as eggs become more likely to contain chromosomal abnormalities. Moreover, this decline becomes progressively steeper after age 35.
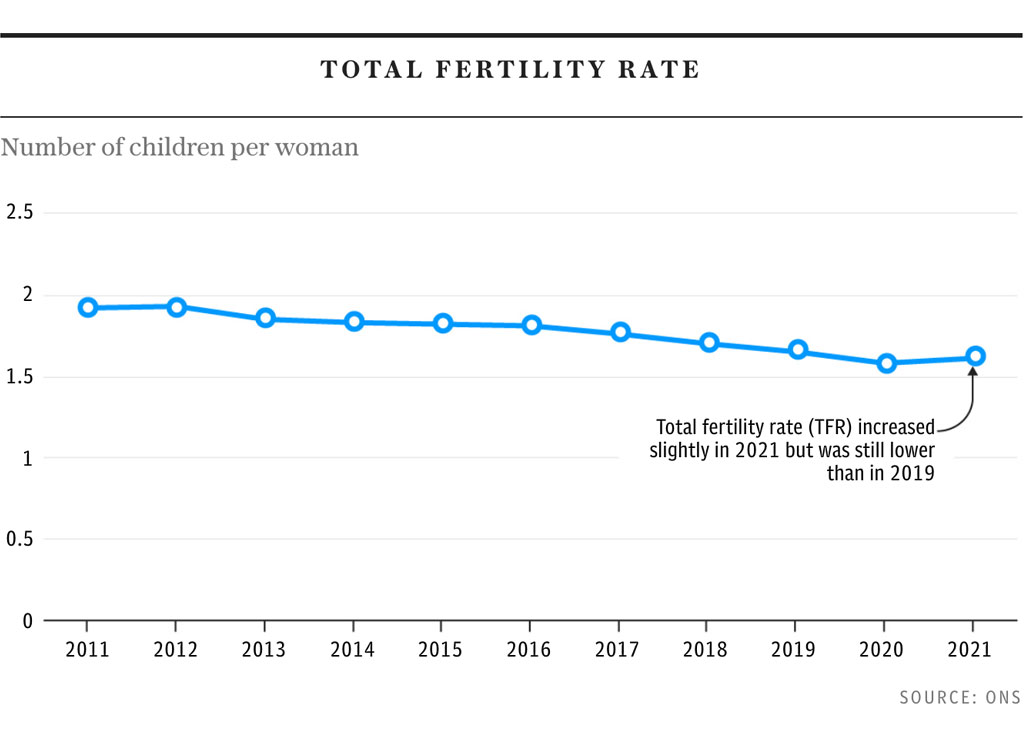
“For somebody who is relatively young, say 35, a six-month or year delay will not make a material difference. But for someone close to 40, a delay of six months might,” says Dr Ray Mathur, a senior fertility consultant and consultant gynaecologist, who is an external adviser to the HFEA and the lead for policy and practice for the British Fertility Society.
When Jane*, 41, saw her GP about treatment in October 2019, she didn’t imagine that more than two years later she would still be waiting. First, her GP forgot to send off her paperwork, meaning she wasn’t in the system until January 2020, and then Covid hit and fertility clinics shut. “By then I was 39 and I was panicking because of the NHS IVF cut-off point of 40,” she says.
As a result of the lost paperwork and delays, Jane and her partner had to repeat the same tests three times before she could even apply for IVF funding. “I put it down to Covid; I was beside myself. I was approaching 40 and we hadn’t got anywhere, I felt like I might lose my chance to have a baby,” she admits.
Fortunately, Jane’s borough, Barnet, offers IVF to women up to the age of 43, so she was still able to access funding for one round of IVF. But when her eggs were finally collected, on 21 August, only one egg was good enough quality to create a viable embryo.
Then, in a further blow, her embryo had to be frozen to avoid ovarian hyperstimulation, since she suffers from polycystic ovaries, which means she is waiting again, with the embryo transfer scheduled for July.
“I feel like an idiot,” she says, tearfully. “If I had gone private, I could have a baby by now. I didn’t have my first egg retrieval until I was 41. Thankfully, in the end, I got one good egg. If it doesn’t work we’ll go private and whack it on a credit card. I’ve been trying to get pregnant since I was 36 and I’m now 42.”
—————-
What to do if you’re struggling to get IVF on the NHS
Access to IVF funding varies according to postcode, with the number of cycles and criteria determined by Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs).
Although the National Institute of Healthcare Excellence (NICE) recommends under‑40s should be offered up to three NHS cycles, some CCGs offer one, or only offer NHS-funded IVF in exceptional circumstances. If you are told you are not eligible for funding, appeal to CCG. The Fertility Network UK website has template letters you can use. Send by recorded delivery.
How to speed things up
Ask your GP about hospital waiting times, as they may vary. In most cases you have the right to choose a hospital – check NHS fertility clinics’ ratings on The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority website: hfea.gov.uk
If you are experiencing long delays and/or are unhappy with your treatment, make a complaint to the CCG.
Best clinics
HFEA rates both private and NHS clinics: hfea.gov.uk/choose-a-clinic/clinic-search
Contact Seed for information about clinics offering IVF with egg donation: seedtrust.org.uk
If you’re thinking about going abroad because the price is lower, Fertility Clinics Abroad lists clinics by countries, with a cost calculator and success rates, though HFEA warns clinics outside the UK may not be regulated: hfea.gov.uk/treatments/explore-all-treatments/fertility-treatment-abroad
Support lines
The Fertility Network UK offers a free support line, open 10-4pm on Monday, Wednesday and Friday: 0121 323 5025; email: support@fertilitynetworkuk.org. On Tuesday and Thursday: 07816 086694; email: janet@fertilitynetworkuk.org.
Info Line: 01424 732361. fertilitynetworkuk.org
—————-
So how long is it sensible to wait? “Where a couple is young it’s reasonable to try for a year, before being referred,” says Mathur. “But where the woman is approaching 40, or there is an obvious cause of infertility, then it’s better for a GP to refer after six months.”
Private treatment is also very costly. Megan’s IVF cost £4,000 including ICSI (intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection), where the sperm is injected into the egg, though the low-cost clinic she used is only available for women under 37. Other UK clinics charge as much as £7,465 per cycle, including blood tests, consultation, medication and two years of storage.
Some women are even seeking treatment abroad where it is cheaper. Spain is the most popular destination, where one round of IVF ranges between £3,043 and £5,664, according to Fertility Clinics Abroad.
Lydia De-Col, 41, who lives in Essex, was nearly denied access to two NHS-funded cycles, after Covid saw her treatment delayed by nine months. She had first applied for funding in February 2020 but didn’t see a consultant until January 2021, by which time she had turned 40, meaning she was only eligible for one round of treatment. “I was devastated,” she says. “What made it worse was the stress of knowing I’d have to go through all those tests again and, on top of that, I’d lose one of my cycles and still not know, after nearly a year, if I’d even be eligible for IVF.”
Lydia successfully appealed the decision and was able to keep two NHS-funded cycles; in the end, she fell pregnant in the first cycle and her baby is due in June. But what about other women on the cusp of the NHS funding limit, who might then lose out on their chance to become mothers?
“It’s our view [at the HFEA] that clinical commissioning groups (CCGs) should have a generous approach to funding patients who have been disadvantaged because of the pandemic,” says Mathur. Yet whether this advice is heeded is at the discretion of each area’s CCG.
While private clinics are now operating at pre-pandemic levels, backlogs remain in the NHS, particularly at preparatory stages of treatment. In the meantime, patients are faced with a difficult choice: continue to wait, perhaps risking their chance of becoming parents, or self-fund costly private treatment. Some health bodies do allow patients to “mix and match” private tests with NHS-funded IVF, but not all do.
“We do hear of people that pay privately for treatments or tests then step back into the NHS system,” says Hill. “But it will be down to your CCG. Our advice is to find what your CCG will allow. It is not an option for everyone and you’ll be bumping others down the list. It’s an incredibly difficult situation to be in.”